 TESTING TOOLS
TESTING TOOLS JIRA: Streamlining Quality Assurance for Bug Reports, Questions, and Project Management

JIRA, developed by Atlassian, is a potent tool that tracks issues and projects. This is why this is a favorite among all QA teams. In this article, we will discuss how JIRA can be used for your everyday operations in QA practice for bug reporting, answering questions, and efficiently managing projects. Also, we will walk through some tips and tricks on how to level up your JIRA experience.
Introduction to JIRA Software-
JIRA is agile project management software that can be used for flexible planning, tracking, and releasing software. It comes with the following features:
- Issue Tracking: helps in developing tasks, bugs, and other work items recording.
- Agile Boards: Scrum and Kanban boards to support agile methodologies.
- Customizable Workflows: Customize workflows to fit specific project needs.
- Reporting: There is support for solid reporting and dashboard capabilities to measure and monitor progress.
- Integration: It is integrated with many other tools and services, thus enhancing its functionality.
Daily Life Usage for a QA: Bug Reporting
1. Bugs Report
For a QA professional, it is of prime importance to report bugs. Following is how it gets streamlined using JIRA:
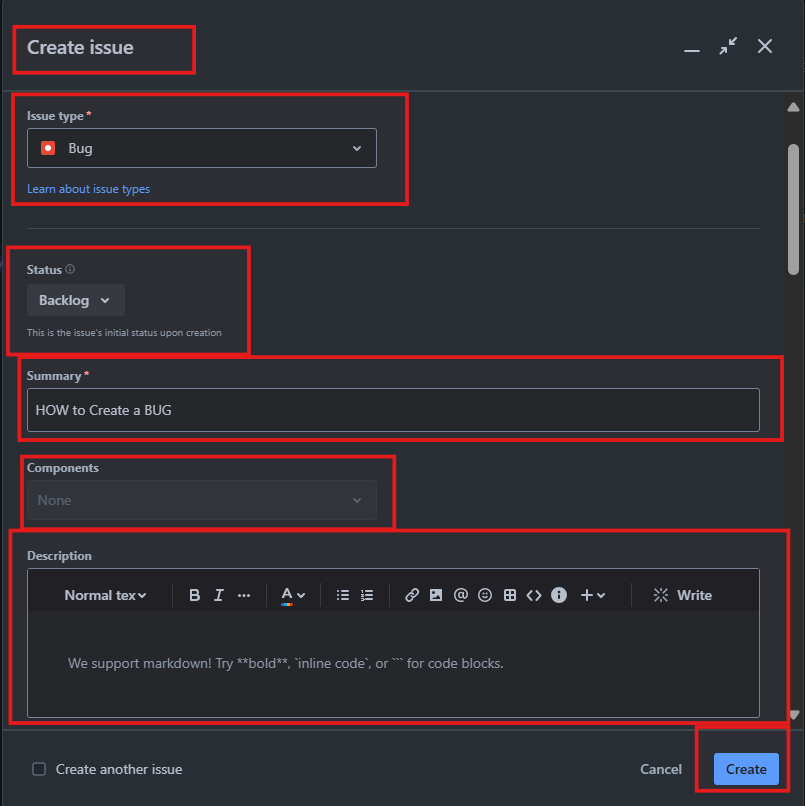
- Create a Bug: In JIRA usually, issues are created for bugs. To create a bug:
- Go to the project where you would like to submit the bug report.
- Click on the "Create" button.
- Select "Bug" from the issue type category.
- Fill in the required fields such as Summary, Description, Steps to Reproduce, Severity, Priority, and Assignee.
- Upload screenshots or log files if necessary.
- Click on "Create" to save the bug.
- Tips:-
- Use Templates: Create bug-description templates for uniformity in detailing the bugs and for completion.
- Link Issues: Relate issues to provide context and increase traceability.
- Custom Fields: Add custom fields to get hold of any information that would be relevant to your team.
2. Track Bug Status
JIRA allows us to monitor the bug status: Open, In Progress, In Review, In QA, QA Passed, and Done. Dashboards and filters will be created to check on the bug's status.
- Tips:
- Custom Workflows: Personalize workflows to suit your testing process.
- Notifications: Set up notifications so that you know the instant critical bugs have a status change.
Responding to Questions
You might need to raise questions or look for clarification on an issue while in your role as QA. One can do this through JIRA by creating new issue types like "Question" or "Clarification."
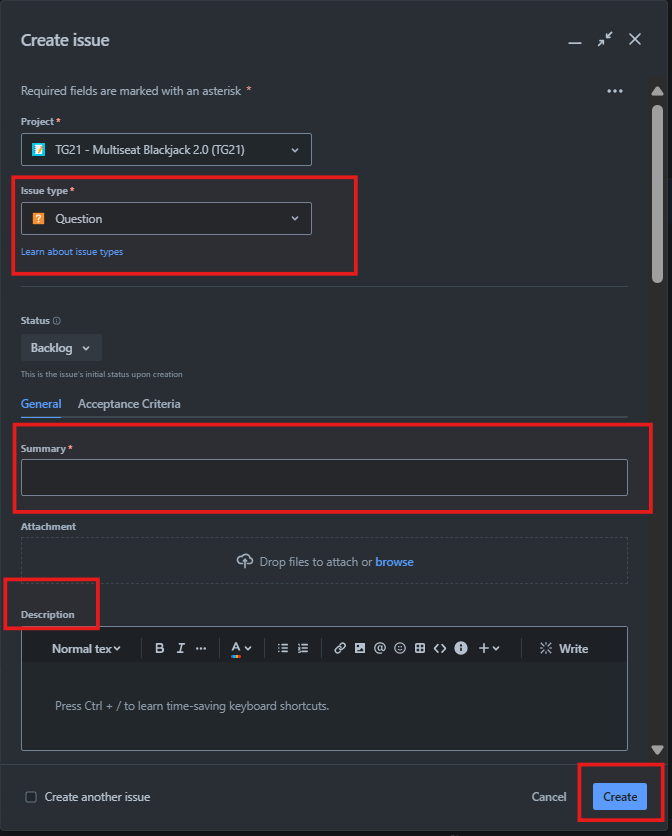
- Steps:
- Create a new issue type called Question.
- Define a workflow that involves statuses Open, Awaiting Response, and Resolved.
- Assign the question to the responsible team member or stakeholder.
- Use comments and attachments to provide context and additional information.
- Tips:
- Labels: Make use of labels to categorize questions, which makes it easier to track them.
- Automation: Configure automation rules to notify assignees about a new question.
Project Management
Project management is embedded in QA projects: planning test cycles, task assignments, and progress monitoring. JIRA can make this process more effective.
1. Planning and Organizing
- Create Epics and Stories: Divide the project into small, easy-to-execute parts using Epics and Stories.
- Sprint Planning: Plan Sprints and assign work with Scrum boards.
- Kanban Boards: Utilize the Kanban boards for handling tasks in an ongoing process and visualizing workflow.
2. Monitoring Progress
- Dashboards: Personalize dashboards to view important numbers such as bug counts, test coverage, and sprint progress.
- Reports: Built-in reports, such as Burndown Charts, Velocity Charts, and Cycle Time reports, provide information on how teams perform.
- Tips:-
- Filters: Set up advanced filters using JQL (JIRA Query Language) to pull data with great precision.
- Roadmaps: Employ roadmaps for high-level project planning and tracking.
Hacks and Pro Tips:
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Get familiar with the keyboard shortcuts of JIRA to be able to move and act quickly: e.g.: 'c' to create an issue, '/', and begin searching. 'g+g' moves to a project fast.
- Bulk Changes: Make bulk changes to many issues in one go, which can save time and is very useful in updating repetitive issues.
- Custom Dashboards: Make your dashboards with gadgets representing what is the most important for you to visualize data.
- Automation: Automate repetitive processes with automation rules, such as issue transitions or sending notifications.
- Add-ons and Plugins: Explore the Atlassian Marketplace for add-ons and plugins that increase the functionalities of JIRA with, for instance, test management tools or better reporting.
Conclusion:
JIRA is one of those tools without which the tasks of QA teams, in terms of bug reporting, questions, or project tracking, get impossible. After exploring some tips and tricks with the features in JIRA, a QA expert can contribute better to completing the software product being developed.
