 OTHERS
OTHERS How End-to-End Testing Enhances User Experience and System Reliability

End-to-end (E2E) testing is a software testing methodology that evaluates the complete workflow of an application from start to finish. It ensures that all integrated components, such as databases, APIs, and UI, function as expected in real-world scenarios. The goal is to simulate real user interactions and verify that the system works cohesively across different layers and dependencies.
Key Components of E2E Testing
1. User Interface (UI) Testing
The UI is the first point of interaction for users, and E2E testing ensures that all elements work as intended.
✅ Example:
- In an e-commerce website, UI testing ensures that users can:
- Click the "Add to Cart" button and see the correct item in the cart.
- Navigate to the checkout page and enter payment details successfully.
- Receive confirmation upon order placement.
2. API Testing
APIs are responsible for data exchange between different system components, such as front-end and back-end services.
✅ Example:
- In a banking application, API testing ensures that:
- The "Check Balance" API correctly retrieves a user's account balance.
- The "Transfer Money" API correctly debits one account and credits another.
- Unauthorized users cannot access sensitive information through API endpoints.
3. Database Testing
Databases store and manage application data. E2E testing ensures data integrity and consistency.
✅ Example:
- In a hospital management system, database testing ensures that:
- Newly registered patients’ details are correctly stored in the database.
- When a doctor updates a patient's prescription, the correct data is reflected in the system.
- Deleted records are removed or archived properly.
4. Third-Party Integration Testing
Many applications rely on third-party services like payment gateways, email services, or social logins.
✅ Example:
- In a ride-hailing app (e.g., Uber, Lyft), E2E testing ensures that:
- Payment processing via PayPal, Stripe, or Google Pay works seamlessly.
- SMS notifications for ride confirmation are correctly triggered.
- Google Maps integration provides accurate navigation for drivers.
5. Workflow & Business Logic Validation
This ensures that the application adheres to business rules and processes.
✅ Example:
- In an HR Management System, testing validates:
- Employees can apply for leave, and managers can approve or reject requests.
- Salaries are calculated correctly based on attendance records.
- Role-based access ensures that only HR personnel can modify employee records.
Why is End-to-End (E2E) Testing Important?
End-to-end testing ensures that the entire application functions as expected by validating real-world workflows, identifying integration issues, and automating critical processes. Below is a detailed breakdown with additional examples.
1. Validates the Entire System Workflow
E2E testing ensures that all subsystems interact seamlessly, verifying the overall business flow.
✅ Example:
- In a food delivery app:
- A customer places an order.
- The system verifies payment via a third-party gateway (e.g., PayPal, Stripe).
- The restaurant receives the order notification and starts preparing the food.
- A delivery driver is assigned, and tracking is provided to the customer.
- The user receives real-time updates on order status.
- In an online education platform:
- A student enrolls in a course and makes a payment.
- The course content is unlocked.
- The system schedules live class notifications.
- The student receives progress tracking and certification upon completion.
2. Detects Integration Issues
E2E testing identifies communication breakdowns between different system modules, ensuring smooth data exchange.
✅ Example:
- In a banking app:
- When a user transfers money, the transaction must be securely processed by an integrated payment gateway.
- The system should correctly deduct the amount from the sender's account and credit it to the recipient’s.
- If the transaction fails, it should roll back without inconsistencies.
- In a travel booking site:
- Flight booking data must sync with third-party airline APIs.
- Integration with payment providers (e.g., Visa, Mastercard) should handle payments securely.
- Users should receive email confirmations upon successful bookings.
3. Mimics Real User Scenarios
Testing should simulate actual user behavior to ensure a flawless experience.
✅ Example:
- In an airline booking system:
- Users search for flights based on date, destination, and price.
- The system provides available options.
- Users select seats, add baggage, and enter passenger details.
- Payment is processed, and a confirmation email with an e-ticket is sent.
- In a ride-sharing app:
- A user requests a ride, and the system matches them with a nearby driver.
- The user can see real-time tracking.
- The system calculates the fare based on distance and time.
- After the ride, the user can rate the driver and receive a receipt.
4. Reduces Manual Effort
Automation in E2E testing saves time, improves efficiency, and ensures consistency across platforms.
✅ Example:
- Automating login testing across different browsers:
- A script tests user login functionality on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
- It validates credentials, session management, and error handling.
- Automated checkout testing on an e-commerce site:
- The script adds products to the cart, applies a discount, and completes payment.
- It verifies order placement, email confirmation, and invoice generation.
Key Components of End-to-End Testing
1. Test Environment Setup
Configuring the test environment, including databases, APIs, network dependencies, and test data, is essential for successful E2E testing.
✅ Example:
- E-commerce Platform:
- Set up test accounts with different user roles (admin, customer, vendor).
- Configure sample credit card details for payment gateway testing.
- Populate the database with sample products and discount codes.
- Banking System:
- Create test user accounts with predefined balances.
- Configure API connections for third-party payment verification.
- Simulate different transaction scenarios (successful, failed, and delayed).
2. Test Case Design
Creating comprehensive test scripts to validate different functionalities and user flows.
✅ Example:
- Password Reset Flow:
- User enters an email address for password recovery.
- The system sends a reset link via email.
- The user clicks the link and sets a new password.
- The system confirms the successful password update.
- Subscription Management:
- Users subscribe to a monthly or yearly plan.
- Payment processing validates card details.
- The system auto-renews subscriptions and notifies users before renewal.
3. Test Execution
Running automated or manual tests to verify system behavior.
✅ Example:
- Manually testing an online chat support feature:
- A customer starts a chat session.
- The chatbot responds with predefined messages.
- If the chatbot cannot resolve an issue, a human agent takes over.
- The conversation history is saved for future reference.
- Automated mobile app testing:
- A script logs into a social media app.
- It posts a status update and verifies whether followers can see it.
- It checks if notifications are triggered correctly.
4. Result Analysis
Evaluating test outcomes to identify bugs and performance issues.
✅ Example:
- Cloud storage system testing:
- Analyze error logs to detect API failures.
- Validate whether file uploads and downloads work correctly.
- Check if file permissions (public/private) are applied correctly.
- Retail Website Performance Testing:
- Monitor server response times during high traffic.
- Analyze checkout failures and payment processing delays.
- Identify UI glitches affecting the user experience.
5. Bug Fixing & Retesting
After identifying defects, developers resolve issues, and testers re-execute tests to confirm fixes.
✅ Example:
- Shopping Cart Issue Fixing:
- A bug where items disappear from the cart after a page refresh is fixed.
- Testers retest the cart function by adding/removing products and checking persistence.
- Payment Gateway Fix:
- A bug causing incorrect tax calculations in an invoice is reported.
- The calculation logic is updated, and test cases are rerun to validate the fix.
How Does End-to-End (E2E) Testing Work?
End-to-end (E2E) testing ensures that all parts of an application work seamlessly together, simulating real-world user interactions. Below is a detailed breakdown with expanded examples of how E2E testing works in an e-commerce application scenario.
Example Scenario: E-Commerce Application
Imagine a user navigating through an e-commerce website, performing key actions such as logging in, searching for products, adding them to the cart, making a payment, and receiving an order confirmation email. E2E testing ensures that each of these steps functions correctly and integrates smoothly with databases, APIs, third-party services, and the user interface.
1. User Login Test
✅ Objective: Verify that a registered user can log in with valid credentials and that incorrect credentials result in the expected error messages.
🔹 Test Cases:
- Valid Login Test:
- Steps:
- Navigate to the login page.
- Enter a registered email and correct password.
- Click on the "Login" button.
- Expected Result: The user is redirected to the homepage/dashboard with a welcome message.
- Invalid Login Test:
- Steps:
- Enter an incorrect email or password.
- Click on the "Login" button.
- Expected Result: The system should display an error message ("Invalid username or password") and prevent access.
- Forgot Password Test:
- Steps:
- Click on "Forgot Password."
- Enter the registered email address.
- Check if the reset password email is sent.
- Expected Result: The user receives an email with a password reset link.
2. Product Search Test
✅ Objective: Ensure that the search functionality returns relevant results and that filtering options work correctly.
🔹 Test Cases:
- Search for an Existing Product:
- Steps:
- Type "wireless headphones" in the search bar.
- Click "Search."
- Expected Result: A list of wireless headphones should be displayed, with correct brand names, prices, and images.
- Search for a Non-Existent Product:
- Steps:
- Type "XYZ Super Phone 5000" (which does not exist).
- Click "Search."
- Expected Result: The system should display "No results found" with a suggestion for similar products.
- Filter Products by Price Range:
- Steps:
- Apply a filter for the price range "$50 - $100."
- Expected Result: The search results should only show products within this price range.
3. Add to Cart Test
✅ Objective: Ensure that users can add, remove, and view items in the cart correctly.
🔹 Test Cases:
- Add Product to Cart:
- Steps:
- Select a product and click "Add to Cart."
- Expected Result: The item should appear in the cart with the correct quantity and price.
- Remove Product from Cart:
- Steps:
- Click on the "Remove" button next to a product in the cart.
- Expected Result: The product should disappear from the cart, and the total amount should update accordingly.
- Cart Persistence Test:
- Steps:
- Add a product to the cart.
- Navigate to another page and return to the cart.
- Expected Result: The product should still be in the cart.
4. Payment Processing Test
✅ Objective: Ensure that the payment system processes transactions securely and correctly.
🔹 Test Cases:
- Successful Payment Test (Credit Card):
- Steps:
- Add items to the cart and proceed to checkout.
- Enter valid credit card details and confirm payment.
- Expected Result: The system processes the payment and redirects the user to an order confirmation page.
- Successful Payment Test (PayPal):
- Steps:
- Choose "PayPal" as the payment option.
- Log in to a PayPal test account and confirm payment.
- Expected Result: The transaction should be successful, and the user should be redirected to the confirmation page.
- Failed Payment Test (Invalid Card Details):
- Steps:
- Enter an incorrect credit card number.
- Click "Pay Now."
- Expected Result: The system should display an error message ("Invalid card details") and prevent payment.
- Payment Gateway Timeout Test:
- Steps:
- Simulate a network delay in the payment gateway.
- Expected Result: The system should handle the delay gracefully and show a message like "Payment processing... Please wait."
5. Order Confirmation Test
✅ Objective: Ensure that users receive an order confirmation email with the correct details.
🔹 Test Cases:
- Verify Order Confirmation Email:
- Steps:
- Complete a purchase.
- Check the registered email inbox.
- Expected Result: An email should be received with order details, estimated delivery time, and contact information.
- Verify Email Content Accuracy:
- Steps:
- Open the order confirmation email.
- Expected Result:
- The email should include:
- ✅ Order number
- ✅ List of purchased items
- ✅ Total cost
- ✅ Estimated delivery date
- ✅ Customer support contact details
- Resend Confirmation Email Test:
- Steps:
- If the user does not receive the email, they request a resend.
- Expected Result: The system should resend the email successfully.
Types of End-to-End Testing and Best Practices
End-to-End (E2E) testing ensures an application works as expected across different components, including UI, APIs, databases, and third-party services. Below is a detailed breakdown of the types of E2E testing with expanded examples and best practices for effective testing.
Types of End-to-End Testing
1. Horizontal End-to-End Testing
✅ Definition:
- This method tests the application's workflow across multiple integrated systems to verify smooth data exchange and functionality.
- It ensures that data flows correctly between different subsystems, such as the front end, backend, databases, and third-party services.
🔹 Example: Online Banking System
Scenario: A customer transfers money from their bank account to another user using an online banking app.
🔸 Test Cases:
- User Login and Authentication:
- Steps: User enters valid credentials and logs in.
- Expected Result: The system verifies the login and grants access.
- Fund Transfer:
- Steps: The user enters the recipient’s account number and amount, then clicks “Send.”
- Expected Result: The system deducts money from the sender’s account and credits it to the recipient’s account.
- Transaction Confirmation and Notification:
- Steps: The system generates a transaction ID and sends a confirmation email/SMS to both users.
- Expected Result: Users receive transaction confirmation messages with the correct details.
- Bank Statement Update:
- Steps: The system updates the sender’s and recipient’s transaction history.
- Expected Result: The transaction appears in both users’ bank statements.
✅ Purpose: Ensure that the entire fund transfer process is smooth and error-free across multiple banking subsystems.
2. Vertical End-to-End Testing
✅ Definition:
- This method tests an application layer by layer to validate that the UI, API, business logic, and database function correctly.
- Focuses on the internal workings of the application rather than system-to-system communication.
🔹 Example: Insurance Claim Processing System
Scenario: A user files an insurance claim, and the system processes it through multiple layers.
🔸 Test Cases:
- User Submits a Claim (UI Layer Test):
- Steps: The user enters claim details (policy number, accident details, and photos) and submits the form.
- Expected Result: The system accepts the input and shows a confirmation message.
- Claim Processing (API & Backend Test):
- Steps: The backend system retrieves claim details and forwards them for review.
- Expected Result: The API correctly fetches data and passes it to the claims processing system.
- Database Update (Database Layer Test):
- Steps: The claim status updates from "Pending" to "Under Review" in the database.
- Expected Result: A database query confirms that the status was updated correctly.
- Final Claim Approval & Payment Processing:
- Steps: The insurance company reviews the claim and processes payment.
- Expected Result: The system triggers a payment request and notifies the user via email.
✅ Purpose: Ensure that the entire process functions correctly across different layers, from the UI to the database.
Best Practices for Effective End-to-End Testing
1. Define Clear Test Scenarios
✅ Why? Covering critical business workflows ensures realistic test coverage.
🔹 Example: Ride-hailing app (Uber, Lyft, etc.)
- Test Case: Booking a ride from point A to point B.
- Steps:
- User enters a pickup and destination location.
- The app calculates the fare.
- The user confirms the ride.
- A driver is assigned.
- Payment is processed after trip completion.
- Expected Result: The ride was completed successfully with a fare breakdown and receipt.
✅ Benefit: It ensures that users experience a smooth and error-free ride-booking process.
2. Use Realistic Test Data
✅ Why? Simulating real-world data helps detect issues that might not appear with dummy data.
🔹 Example: Video Streaming Service (Netflix, Hulu, etc.)
- Test Data:
- Standard Account: Limited to 720p streaming.
- Premium Account: Supports 4K streaming.
- Parental Control Account: Blocks certain content.
- Test Case: Ensure that content restrictions and quality settings apply correctly to different account types.
✅ Benefit: It prevents issues where users receive incorrect service features.
3. Automate Repetitive Tests
✅ Why? Automation speeds up testing, especially for repetitive tasks like login, checkout, and UI interactions.
🔹 Example: E-Commerce Website (Amazon, eBay, etc.)
- Scenario: Automate login across multiple devices and browsers.
- Tools: Use Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright to test:
- Log in with valid credentials.
- Login with invalid credentials.
- Remember-me functionality.
✅ Benefit: It ensures cross-browser compatibility without manual testing.
4. Monitor System Performance
✅ Why? Identifies performance bottlenecks before users experience slow response times.
🔹 Example: News Website Handling High Traffic
- Scenario: Simulate thousands of users accessing a news website at the same time.
- Test Case: Check if the page loading time remains within acceptable limits (e.g., <2 seconds).
- Tool: Use JMeter or Gatling for load testing.
✅ Benefit: Prevents server crashes and slowdowns during peak usage.
5. Implement CI/CD Integration
✅ Why? Ensures E2E tests run automatically after every code update before deployment.
🔹 Example: Mobile Banking App
- CI/CD Pipeline Setup:
- The code is pushed to GitHub/GitLab.
- Automated tests run in Jenkins/GitHub Actions.
- Tests validate login, fund transfer, and statement updates.
- If tests pass, deployment proceeds.
✅ Benefit: It reduces production bugs and ensures continuous software stability.
6. Regularly Update Test Cases
✅ Why? Applications evolve, and test cases must be updated to cover new features and UI changes.
🔹 Example: Online Payment App (PayPal, Stripe, etc.)
- Scenario: A new payment method (Cryptocurrency) is introduced.
- Test Case Updates:
- Verify that cryptocurrency payment works correctly.
- Ensure refunds and transaction history updates properly.
- Test fraud detection for crypto transactions.
✅ Benefit: It keeps test coverage relevant to current application features.
Common Challenges in End-to-End (E2E) Testing and Solutions
E2E testing is essential for ensuring that an application functions seamlessly across all components. However, it comes with several challenges. Below, we will expand on each challenge, provide real-world examples, and discuss solutions to mitigate them.
1. Complex Test Environment
✅ Challenge:
- Managing dependencies across multiple integrated systems, such as databases, APIs, third-party services, and networks.
- Setting up a stable test environment that mirrors the production environment is challenging.
🔹 Example: E-Commerce Platform
- Scenario: Testing an online store requires dependencies like:
- Inventory system (to check product availability).
- Payment gateway (to process payments).
- Shipping service (to calculate delivery estimates).
- Issue: If any of these services fail, tests may not execute properly.
✅ Solution:
- Use cloud-based testing environments (e.g., AWS, Azure, or Docker) to easily replicate production-like conditions.
- Use service virtualization to simulate third-party systems and avoid real-time dependency failures.
- Automate environment setup with Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) using Terraform or Kubernetes.
2. High Maintenance Cost
✅ Challenge:
- UI changes and feature updates break automated scripts, requiring frequent updates.
- Maintaining large-scale E2E test suites is expensive and time-consuming.
🔹 Example: Social Media Platform (Facebook, Twitter, etc.)
- Scenario:
- The UI of the "Post" button changes from button[class='post'] to button[class='publish'].
- Automated tests using the old selector fail, requiring updates.
- Issue: Updating test scripts manually for every minor UI change is inefficient.
✅ Solution:
- Use modular test automation frameworks like Page Object Model (POM) to minimize code duplication.
- Leverage AI-based automation tools (e.g., Testim, Mabl) that adapt to UI changes dynamically.
- Implemented version control for test scripts to track changes efficiently.
3. Slow Execution Time
✅ Challenge:
- Running a full E2E test suite takes a long time, delaying the development cycle.
🔹 Example: Online Banking Application
- Scenario: A full E2E test covering login, fund transfers, and account statements takes 3+ hours to execute.
- Issue: Slow test execution increases the time-to-market and disrupts continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
✅ Solution:
- Use parallel testing:
- Run multiple tests simultaneously using Selenium Grid, TestCafe, or Playwright.
- Run tests based on priority:
- Use test categorization (e.g., critical, medium, low) to run only necessary tests during CI/CD.
- Use headless browsers (Chrome, Firefox headless) to execute UI tests faster.
4. Flaky Tests
✅ Challenge:
- Flaky tests are inconsistent, sometimes passing and sometimes failing due to unstable environments, network latency, or dynamic UI elements.
🔹 Example: Ride-hailing app (Uber, Lyft, etc.)
- Scenario: A test script checks if a driver is assigned within 5 seconds, but due to network delays, it sometimes fails.
- Issue: Dynamic elements (e.g., loading spinners, pop-ups) cause unreliable test execution.
✅ Solution:
- Implement retries:
- If a test fails, re-run it before marking it as failed.
- Example: cy.get('button').click({ timeout: 10000 }) (Cypress wait mechanism).
- Use intelligent waits:
- Instead of fixed delays (sleep(5s)), use explicit waits (waitUntil(element.isVisible)).
- Stabilize test data:
- Use a dedicated test database to avoid changes in production data affecting test outcomes.
Best Tools for End-to-End Testing
Choosing the right E2E testing tool depends on the type of application (web, mobile, or API) and the required features. Below are some popular E2E testing tools along with their key features and examples.
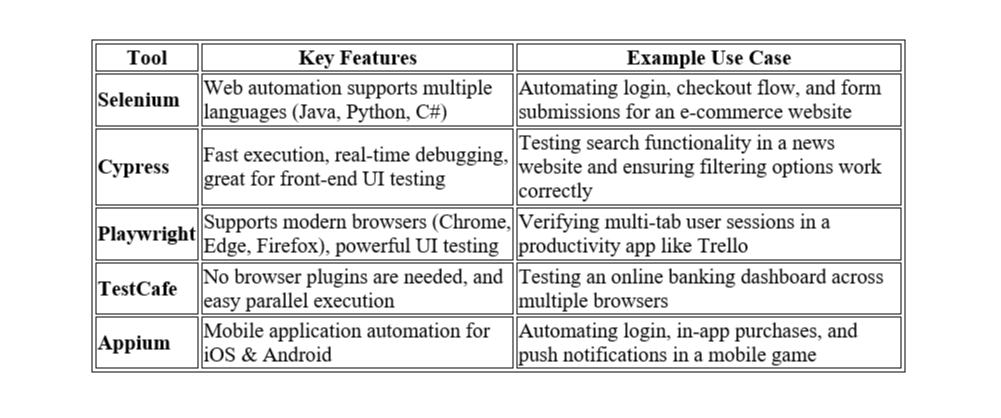
Detailed Tool Comparison and Use Cases
1. Selenium (Best for Cross-Browser Testing)
✅ Why use it?
- Automates web applications across multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge).
- Supports various programming languages (Java, Python, C#, Ruby).
🔹 Example:
- Scenario: Testing an online retail store’s checkout process on Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
- Solution: Use Selenium Grid to execute tests in parallel across multiple browsers.
2. Cypress (Best for Fast and Reliable UI Testing)
✅ Why use it?
- Executes tests directly in the browser for faster execution.
- Great for front-end testing of JavaScript-based applications.
🔹 Example:
- Scenario: Testing a real-time chat application to verify that messages are displayed instantly.
- Solution: Use Cypress real-time debugging to inspect network responses.
3. Playwright (Best for Modern Browser Testing)
✅ Why use it?
- Supports multi-browser and multi-tab testing.
- Handles UI interactions with ease.
🔹 Example:
- Scenario: Testing a dashboard application where users can open multiple tabs and perform actions.
- Solution: Use Playwright’s multi-context feature to simulate multiple users interacting with different tabs.
4. TestCafe (Best for Simple Web Testing Without Plugins)
✅ Why use it?
- No need for WebDriver or browser extensions.
- Supports parallel test execution out of the box.
🔹 Example:
- Scenario: Testing a user profile update feature in a job portal website.
- Solution: Use TestCafe's parallel execution to test on different browsers simultaneously.
5. Appium (Best for Mobile App Testing)
✅ Why use it?
- Automates iOS and Android applications.
- Supports real devices and emulators.
🔹 Example:
- Scenario: Testing an e-wallet mobile app to verify if users can send payments and receive notifications.
- Solution: Use Appium’s device cloud to run tests on multiple devices at once.
Conclusion
End-to-end testing is a critical part of software development that ensures a smooth, error-free user experience. By following best practices, using the right tools, and addressing common challenges, organizations can enhance their application reliability and efficiency. Investing in a well-structured E2E testing strategy helps improve software quality and customer satisfaction.